Performance management refers to the systematic process through which an organization improves its employees' performance by setting clear expectations, providing feedback, coaching, and assessing progress. It focuses on aligning individual goals with the organization’s objectives, helping employees
What is Performance Management?
Performance management is a continuous process that intends to improve employees' performance through setting unambiguous expectations, monitoring progress, giving feedback, and providing development opportunities. It aligns individual goals with the objectives of the organization, enhances productivity, and promotes employee growth. The major activities are goal setting, performance appraisals, coaching, and career development. In a well-structured performance management system, there would be improved engagement, job satisfaction, and overall success of an organization.
The Performance Management Process
A well-structured performance management process can significantly impact employee engagement and productivity. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key steps:
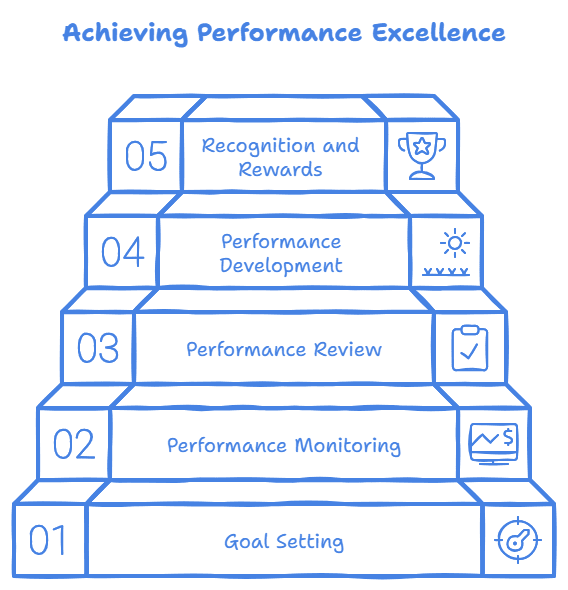
Goal Setting:
Smart Goals: Ensure goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Alignment: Align individual goals with team and organizational objectives.
Collaboration: Involve employees in the goal-setting process to foster ownership and commitment.
Performance Monitoring:
Regular Check-ins: Conduct regular one-on-one meetings to discuss progress and provide feedback.
Performance Tracking: Use performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor progress.
Real-Time Feedback: Provide timely feedback to address issues and celebrate successes.
Performance Review:
Formal Reviews: Conduct formal reviews at regular intervals to assess performance against goals.
Informal Reviews: Conduct informal check-ins throughout the year to provide ongoing feedback.
Self-Assessment: Encourage employees to reflect on their performance and identify areas for improvement.
Performance Development:
Identify Development Needs: Identify skills gaps and areas for improvement based on performance reviews.
Create Development Plans: Develop personalized development plans to address specific needs.
Provide Opportunities: Offer training, coaching, and mentoring opportunities to support development.
Recognition and Rewards:
Public Recognition: Recognize and celebrate achievements publicly to boost morale.
Non-Monetary Rewards: Offer non-monetary rewards like bonuses, promotions, and flexible work arrangements.
Monetary Rewards: Consider performance-based pay and bonuses to incentivize high performance.
Performance Management: EasyHR's Guiding Principles
To ensure the effectiveness of performance management, consider the following guiding principles:
Fairness and Consistency: Apply performance standards consistently and fairly to all employees.
Transparency and Communication: Maintain open and transparent communication throughout the process.
Focus on Development: Use performance reviews as opportunities for growth and development.
Positive Reinforcement: Recognize and reward positive performance to motivate employees.
Two-Way Communication: Encourage open and honest dialogue between managers and employees.
Review: Guiding Principles
Effective performance reviews are essential for driving performance improvement. Here are some guiding principles for conducting effective reviews:
Focus on Behavior and Results: Assess both the employee’s behavior and their outcomes.
Be Specific and Objective: Use specific examples to illustrate performance.
Balance Positive and Negative Feedback: Provide both positive reinforcement and constructive criticism.
Involve the Employee: Encourage the employee to participate actively in the review process.
Set Clear Expectations: Establish clear expectations for future performance.
Additional Methods for a Fully Rounded Performance Evaluation
To gain a comprehensive understanding of an employee’s performance, consider incorporating additional methods into your performance evaluation process:
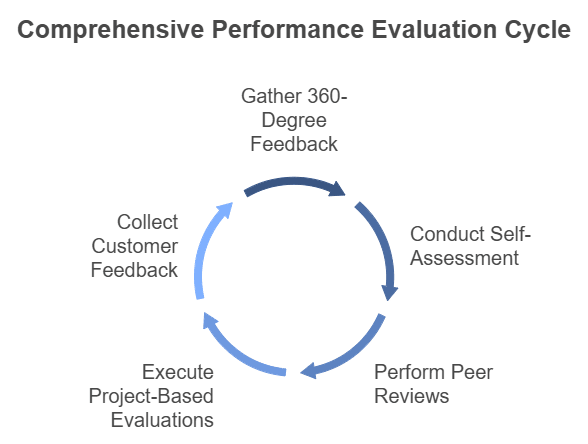
360-Degree Feedback: Collect feedback from multiple sources, including peers, subordinates, and supervisors.
Self-Assessment: Encourage employees to reflect on their performance and identify areas for improvement.
Peer Reviews: Have peers assess each other’s performance.
Project-Based Evaluations: Evaluate performance on specific projects or tasks.
Customer Feedback: Gather feedback from customers to assess the impact of the employee’s work.
Conclusion
Effective performance management is a critical driver of organizational success. By implementing a well-structured performance management process, organizations can create a culture of high performance, employee engagement, and continuous improvement. Remember, performance management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Tailor your strategies to the specific needs of your organization and its employees.
For more information on Performance management with EasyHR, visit easyhrworld.com.
