The Key Role of Human Resource Management in Driving Organizational Success
The Key Role of Human Resource Management in Driving Organizational Success
In today's highly competitive business landscape, the role of human resource management (HRM) has become more critical than ever in driving organizational success. HRM is not just about hiring and managing employees; it encompasses a wide range of strategic activities that are crucial for achieving business objectives.
A strong HRM strategy is essential for attracting top talent, developing employee skills, and fostering a positive work culture. It involves designing effective recruitment and selection processes, implementing robust training and development programs, and creating performance management systems that reward and motivate employees.
By prioritizing the well-being and development of its workforce, an organization can enhance employee satisfaction, engagement, and retention. This, in turn, leads to increased productivity, better customer service, and ultimately, improved business performance.
Furthermore, HRM plays a vital role in fostering diversity and inclusion, promoting fairness and equality within the workplace. By embracing a diverse workforce, organizations can tap into a broader range of perspectives and ideas, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
In conclusion, effective HRM is more than just a department within an organization. It is a strategic function that can make a significant impact on business success. By investing in their people and designing effective HRM strategies, organizations can create a culture of excellence and drive sustainable growth.
Simplified Understanding of HRM's Role in Organizational Success
Foundation for Growth: HRM acts as the backbone, aligning workforce strategies with business goals to drive performance.
Beyond Basics: It goes beyond traditional roles like hiring, focusing on enhancing productivity, innovation, and competitive advantage.
Comprehensive Management: Manages recruitment, culture, and employee well-being, fostering motivation and engagement.
Proactive Strategy: Integrates with business plans to address challenges such as turnover and skill gaps.
Collaboration: Partners with other departments to ensure cohesive efforts towards organizational success.
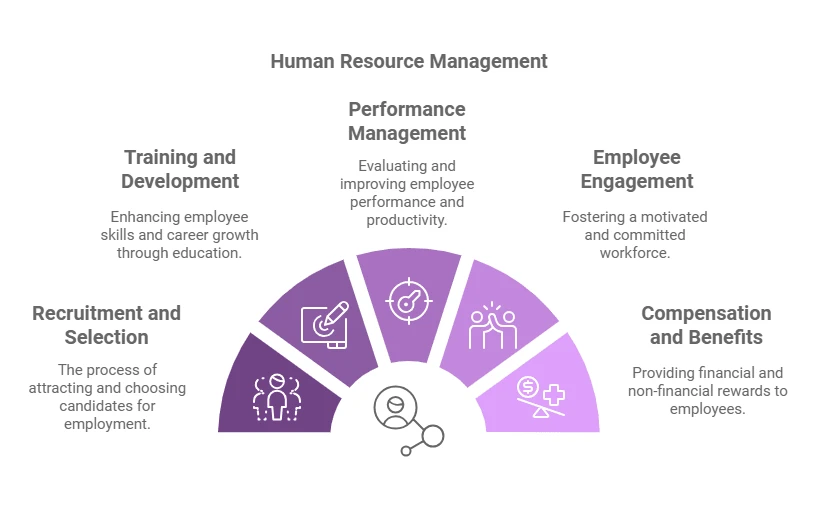
Key Functions of HRM
Recruitment and Selection
Training and Development
Performance Management
Employee Engagement
Compensation and Benefits
Recruitment and Selection: Finding the Right Talent
Identifying organizational needs:
Define roles, responsibilities, and required skills.
Create detailed job descriptions to attract qualified candidates.
Selection Process:
Conduct interviews, assessments, and background checks.
Use behavioral interviews to evaluate problem-solving and interpersonal skills.
Include diverse panels to mitigate biases and ensure fairness.
Continuous Improvement:
Use metrics like time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, and retention rates to refine strategies.
Adapt processes to consistently attract and retain top talent in a competitive market.
Training and Development: Enhancing Employee Skills and Knowledge
Focus on Workforce Capabilities:
Improves job-specific skills and fosters a culture of learning.
Leads to higher job satisfaction, productivity, and reduced turnover.
Types of Training Programs:
Onboarding: Helps new employees adapt to organizational culture.
Skill Development: Includes technical, leadership, and soft skills training.
Tailored Development Opportunities:
Mentorship programs, online learning platforms, and industry conferences.
Impact on the Organization:
Builds a skilled, adaptable, and motivated workforce.
Boosts morale, engagement, and organizational performance.
Performance Management: Setting Goals and Evaluating Performance
Goal Setting:
Collaboratively set
SMART goals
(Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
Align individual goals with organizational objectives.
Ongoing Feedback:
Conduct regular check-ins and progress reviews.
Adjust goals and provide direction to keep employees on track.
Comprehensive Evaluations:
Use self-assessments, peer reviews, and manager evaluations for a holistic view.
Provide constructive feedback to help employees improve.
Fostering Culture:
Encourage accountability and open communication.
Promote continuous improvement and engagement to build high-performing teams.
Employee Engagement and Retention: Creating a Positive Work Environment
Encouraging Open Communication:
Promote transparency and dialogue through town halls, feedback sessions, and surveys.
Foster trust and a sense of belonging by valuing and acting on employee feedback.
Recognizing Contributions:
Implement recognition programs to celebrate individual and team achievements.
Use formal awards, public acknowledgments, or small gestures to boost morale and motivation.
Building a Supportive Culture:
Create an environment where employees feel valued and supported.
Enhance engagement by addressing employee needs, promoting collaboration, and celebrating successes.
Employee Benefits and Compensation: Motivating and Rewarding Employees
Attractive Compensation Packages:
Design competitive pay structures based on market trends, performance, and profitability.
Include performance-based bonuses and incentives to motivate exceptional contributions.
Comprehensive Benefits:
Offer benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and wellness programs.
Focus on work-life balance to enhance employee well-being and satisfaction.
Retention and Engagement:
Use salary benchmarking and reviews to maintain fairness and competitiveness.
Show commitment to employees' needs, fostering loyalty and reducing turnover.
HRM and Organizational Culture: Shaping Values and Behaviors
Defining Organizational Culture:
Culture reflects shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that guide how work is done and interactions occur.
HRM's Role:
Implement core values and embed them in recruitment, onboarding, and performance management.
Promote diversity, inclusion, and open communication to create a cohesive environment.
Evolving Culture:
Monitor and adapt culture based on leadership changes, market dynamics, and employee feedback.
Conduct surveys and assessments to identify and address gaps in alignment.
Impact:
Drives employee engagement, collaboration, and innovation, leading to organizational success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective Human Resource Management (HRM) is essential to organizational success. It drives performance through strategic functions like recruitment, training, performance management, and compensation. HRM also shapes organizational culture, fosters employee engagement, and supports innovation. By aligning the workforce with company goals and nurturing employee development, HRM helps organizations thrive in a competitive environment. A strong HRM strategy leads to sustainable growth, ensuring businesses can adapt to challenges and maintain high performance. Effective HRM is, therefore, a cornerstone of organizational success.




